First off, what is SEO?
Search engine optimization (SEO) is the process of affecting the visibility of a website or a web page in a search engine’s unpaid results – often referred to as “natural,” “organic,” or “earned” results.
We all get those annoying Indian ‘SEO Consultants’ emailing us, promising the world but delivering nothing, so here is a real explanation of onsite SEO:
Think of Google as a library, and your website is a book in that library. Google want its ‘books’ to be logically organized and properly structured: a title, chapters, sub-chapters, relevant content and photos. An example would be a biology textbook, where you might have a title such as “Marine Biology” as your chapter title (H1 heading in SEO), followed by a title for a subchapter, like “Mammals” (an example of a H2 heading). After you have your headings, you then have your relevant content, and properly captioned (or tagged) images.
What happens when your ‘book’ isn’t to Google’s liking is that Google will give you a lower score.
Why does your score matter?
Well, your website score is important because it helps dictate where you are placed in the organic listings (order of search results), as well as inorganic search results such as Google Adwords.
Let’s have a look at how the position of your website affects how many people will click on it – this data is from January 2016:
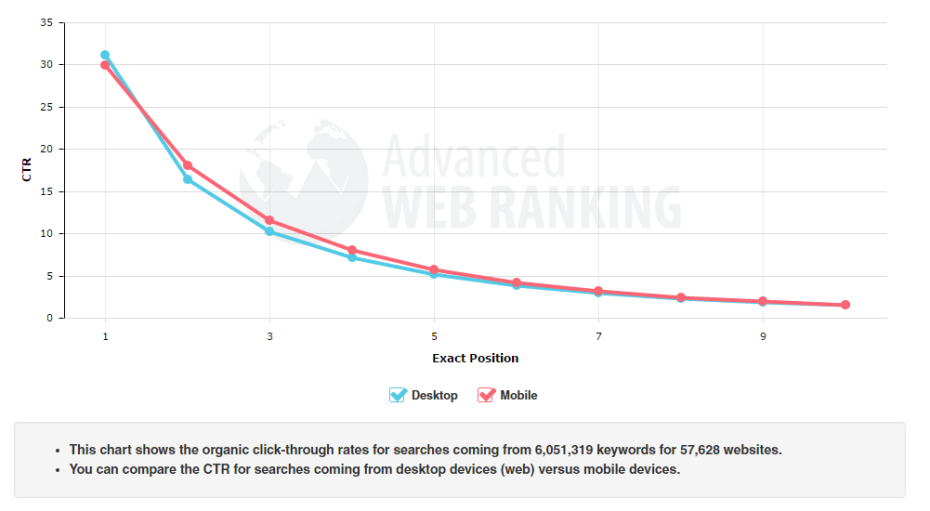
As you can see through this data, the higher position you are in Google, the more clicks you get, and thus, the more traffic & sales you drive to your website.
So now that you know what onsite SEO is, and why it’s important, how does it actually get done?
There is a whole lot to onsite SEO, everything from duplicate content, canonical tags, hreflang tags, and more. But really, on the surface, onsite SEO doesn’t have to be so complex. I have broken it down in to 4 steps.
- Think like Google.
Google needs to know what your business is, and what it does. Google won’t just take your word for it, so it will look through keywords in the content of your website. In the next section I will talk about those keywords in more detail, but let’s focus on placement first.
If you get nothing else from this post, ensure that you place the core keywords in your title, description, h1 and p tags. Having said that, make sure you don’t overuse them, as google will penalize you for “keyword stuffing”. The best way to avoid keyword stuffing is to place keywords in naturally, in a way that aids your user’s experience.
Time to explain a few of these elements:
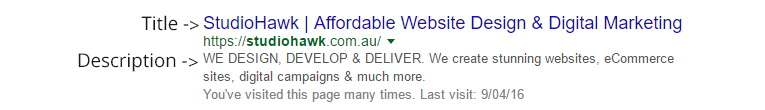
- Title: The blue hyperlink on Google, and the actual title for the website’s window. This can be found in the <title> section of your websites code
- Description: this is the description line on Google. This is where it’s important to think from the perspective of your user – don’t just use keywords, give them a reason to click on your website. This can be found in your code under: //meta name=”description” content=”your description goes here”//
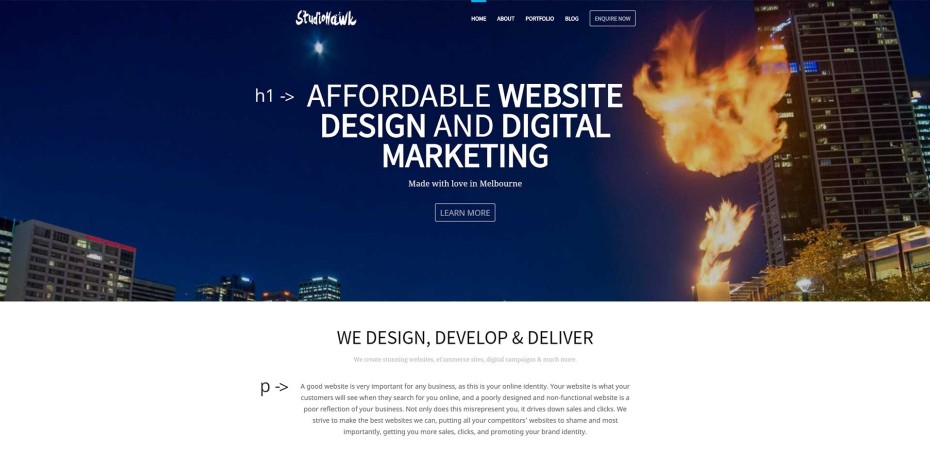
- h1 Tag: This is used to indicate the main heading of your page, and should give information about what the page is. E.g. “Affordable plumbing in Melbourne”. Make sure that this uses the keyword you are targeting and matches the wording of the description and title. In your code, it will look like: <h1> Content goes here </h1>
- p Tag: This is the paragraph tag, usually used in the body of the page where the actual content of the website goes. In the code, this will look like <p> Content goes here </p>
Don’t be intimidated by the code, if you have any questions, we are here to help – just leave a comment below.
Below is an example of all these elements in play, so you can get a visual idea of how they relate to each other and what they look like when done right.
Other considerations:
– Make sure that you have a site map
– Make sure that your website is optimized for Mobile
– Ensure that there is no JavaScript or code obstructing Google’s vision when trying to find you content.
– If you offer localized services, use webmaster tools to ensure that you are set to the correct country.
- Think like a Googler.
It’s not enough to just make Google happy, you need to think like a user on Google.
The first thing you need to do is identify who you are targeting, then you need to identify what they are typing in to Google to search for products/services like yours. Think what kind of action, description or product word they might be looking for, remember that 500,000,000 of searches every day have never been seen by Googles search engine before¹.
The key here is to find what keywords really work for you. Sure you can try to cater for a thousand different keywords, but it’s far better to rank #1 for a handful of keywords than rank #1000 for a thousand.
Once you have identified your keywords, and you’ve put them in the right spots (title, meta description, h1, etc.) then it’s time to ensure that you write in a human, natural way. I will let you in on a secret, use this article as an example. Within the first paragraph (which will have a <p> tag) I used the terms that I was targeting such as: SEO, What is SEO, Search engine optimization.
I use these terms in the title, and description. Note it is natural in voice, whilst still strategic in placement and content.
- Write content that helps your users.
It makes sense right? Content is immensely powerful, it gives you the opportunity to answer your user’s question, or guide them through your product or service. Each new piece of content could be the one that a user discovers and uses as a funnel to your product or service.
This is why you need to identify what kind of users you want to attract, and think about what kind of content that they will find useful. Some good examples are tutorials, getting started guides, and reviews. The key is that content is high quality, and hyper relevant. Spend time crafting content that is truly unique, and you will be rewarded through organic growth, including social sharing.
- Get yourself out there!
It’s important that you actually publish your website and content. As I said earlier, Google scores a page based on not only they’re on site SEO, but also based on how many backlinks there is to it.
Backlinks themselves are a little out of the scope of this blog post, but all you need to know is that it’s all about quality not quantity. A highly relevant backlink on an authoritative domain is far more beneficial than 10,000 spammy ones you purchase, for example on Fiverr, which will penalize you.
Final word –
SEO doesn’t just happen overnight, there is no silver bullet, but if you provide content that genuinely helps your users, Google will notice you. Remember that this is just the tip of the iceberg in the world of SEO, and that you can never know everything.
If you need any help with setting up your onsite SEO, or simply need some advice, please leave a comment below and I would be more than happy to help.
________________________________
¹ [Jon Wiley, Google search lead designer – http://readwrite.com/2012/02/29/interview_changing_engines_mid-flight_qa_with_goog/#awesm=%7EoiNkM4tAX3xhbP]